Lung lobe Torsion
27 April, 2021
Case example
A case with a twist
A 10- year-old schnauzer was presented with a chronic cough of months duration
CT findings
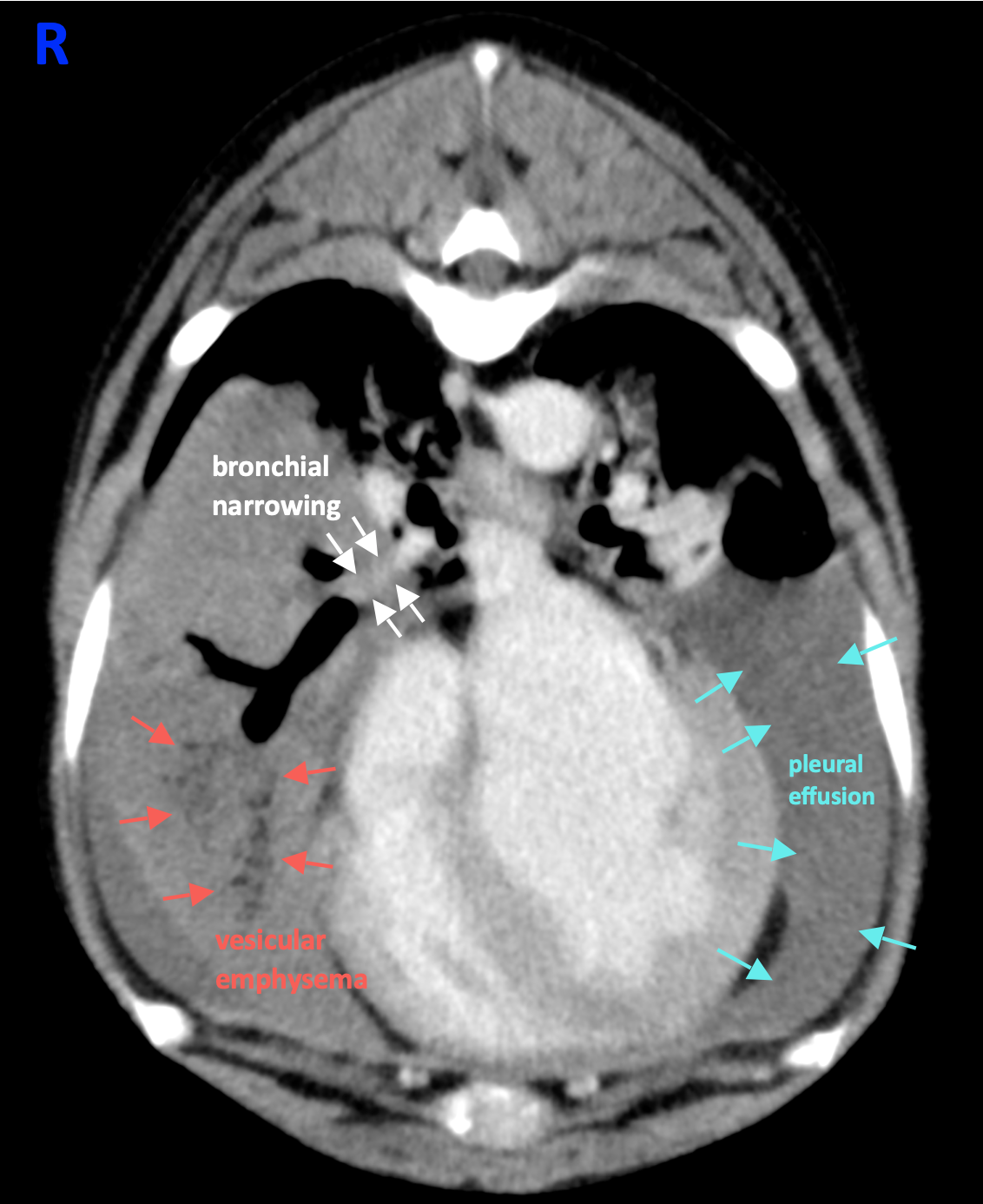
- A large amount of fluid attenuating material is within the dependent aspect of the pleural space bilaterally. (Image 1)
- The right middle lung lobe is enlarged, and its bronchial lumen is focally, completely narrowed. (Image 1)
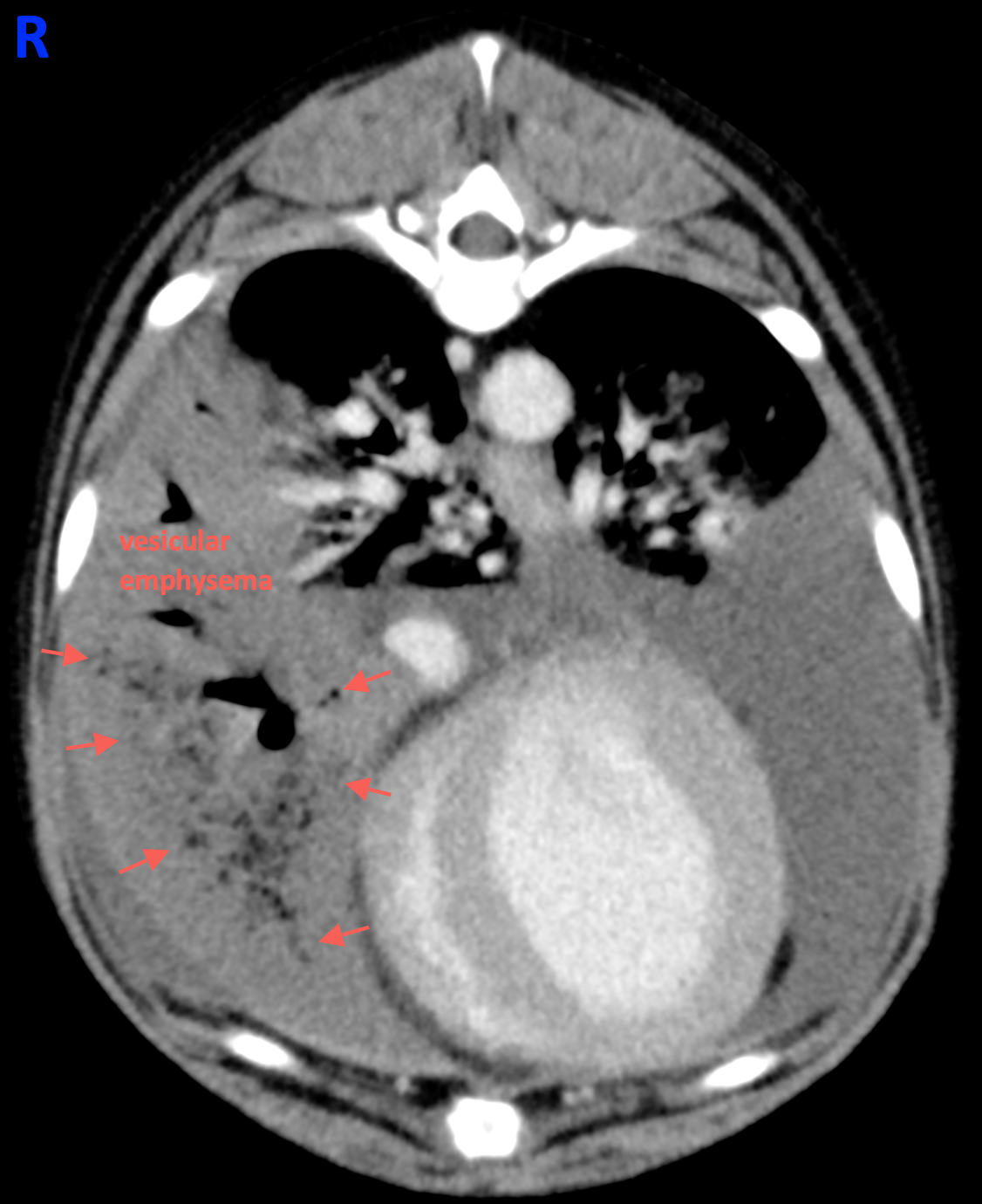
- Vesicular emphysema and a focally enlarged bronchus are also associated with this lung lobe. (Image 2)
- The right middle pulmonary parenchyma is non-contrast enhancing.
Conclusions
- Conclusions: Lung lobe torsion of the right middle lobe with bilateral pleural effusion
Learning points
- The right middle lung lobe is the most commonly affected lobe in large breed dogs.
- Radiographic und CT characteristics: Enlargement and consolidation of the affected lung lobe, vesicular emphysema, lack of contrast enhancement, secondary pleural effusion
More information
- Radiographs vs CT: pathognomonic focal narrowing of the bronchus on CT
- »Computes tomographic features of lung lobe torsion.«
— Vet Radiol Ultrasound 2008;49(6):504-8. - »Usefulness of CT imaging for segmental lung lobe torsion without typical radiographic imaging in a Pomeranian.«
— J Vet med Sci 2015;77(2):229-31. - »Radiographic diagnosis of lung lobe torsion.«
— Vet Radiol Ultrasound 2005;46(6):478-484.
Images courtesy of the Tierklinik Bockenheim, Germany.
UPLOAD MEDICAL IMAGES NOW

